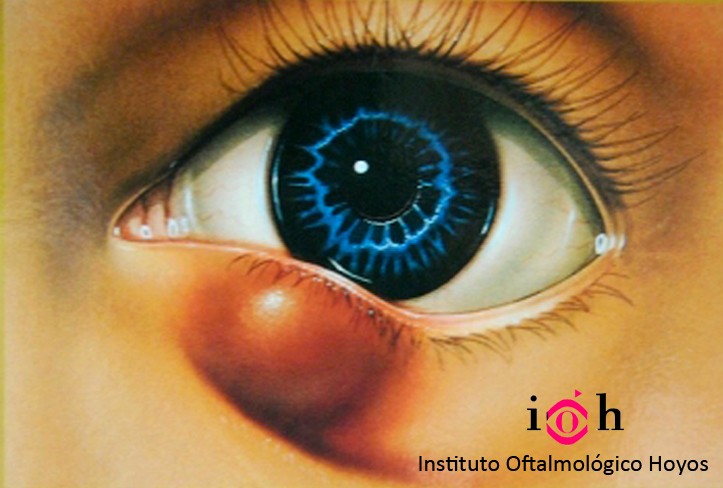
STYES AND CHALAZION
A little protuberance on the eyelid caused by a blockage in a small sebaceous gland.
Causes, incidence and risk factors.
A chalazion develops inside the Meibomian glands, which are in charge of producing the fatty part of the tear film which lubricates the eye. The eyelid has approximately 100 of these glands distributed between the upper and lower eyelid and they are located near the eyelashes.
A chalazion is caused by an obstruction of the duct which drains one of these glands.
Symptoms :
-Sensitivity in the eyelid
-Increase in tearing
-Painful inflammation of the eyelid
-Sensitivity to light
-Blurred vision
Treatment :
The primary treatment is the application of dry heat for 10 to 15 minutes, 3 to 4 times a day, which may soften the hardened oils which are obstructing the duct and encourage it to drain and heal.
If the chalazion continues to grow, or becomes a cyst, it is possible that it will have to be surgically removed in the doctor’s surgery. This is done through the internal part of the eyelid to avoid scarring the skin. The operation takes approximately 10-15 minutes.
After surgery, dry cold should be applied locally and antibiotic and anti-inflammatory drops are prescribed during the first week.
Complications:
A large chalazion can cause astigmatism due to pressure on the cornea, but this improves when treatment is carried out.
Prevention :
Adequate cleaning of the eyelids for those people who have a propensity to chalazions can prevent the reappearance of this condition. In addition to this, cleaning the eyelash area with special wipes, soapy gels or baby shampoo can help to reduce obstructions in the ducts.